Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Plantae
Magnoliophyta
Liliopsida
Commelinales
Commelinaceae
- General
- Distribution
- Impact
- Management
- Bibliography
- Contact
Common name
riri raei (English, Cook Islands), moses in a boat (English), riri mangio (English, Cook Islands), oyster plant (English), boat lily (English), Moses-in-a-basket (English, Hawaii), talotalo, laupapaki (English, Niue), faina kula (English, Tonga), boat plant (English)
Synonym
Rhoeo discolor , Hance ex Walp
Rhoeo spathacea , (Sw.) Stear
Tradescantia discolor , L'Hér.
Rhoeo spathacea , (Sw.) Stearn
Rhoeo spathacea , (Sw.) Stearn forma concolor (Baker) Stehle
Rhoeo spathacea , (Sw.) Stearn forma variegata(Hook) Stehle
Tradescantia discolor , L'Hér. var. concolor Baker
Tradescantia discolor , L'Hér. var. variegata Hook.
Tradescantia discolor , L'Hér.
Rhoeo discolor , (L'Hér.) Hance
Rhoeo spathacea , (Sw.) Stear
Tradescantia discolor , L'Hér.
Rhoeo spathacea , (Sw.) Stearn
Rhoeo spathacea , (Sw.) Stearn forma concolor (Baker) Stehle
Rhoeo spathacea , (Sw.) Stearn forma variegata(Hook) Stehle
Tradescantia discolor , L'Hér. var. concolor Baker
Tradescantia discolor , L'Hér. var. variegata Hook.
Tradescantia discolor , L'Hér.
Rhoeo discolor , (L'Hér.) Hance
Similar species
Summary
Tradescantia spathacea is a beautiful succulent that has been introduced to south Asia and many Pacific Islands from its native range in the tropical Americas. Although it has not yet been declared a pest, in many areas it has become a very invasive weed, especially in Florida where it invades and disrupts native plant communities. Tradescantia spathacea creates a dense groundcover on the forest floor which prevents native plants from germinating. Tradescantia spathacea has diverse reproductive methods and grows in areas other plants cannot. These two characteristics make this plant a potential danger to many areas. Monitoring is recommended wherever this species is present.
Species Description
\"Rosette-forming succulent herb, stems short, leaves crowded, elongate, broadly linear-lanceolate, up to 30-40cm long and 4-6cm wide, the upper surface green, the lower surface rich reddish-purple; inflorescence axillary, short; bracts subsessile, boat-shaped; flowers white; petals 3; stamens 6, ovary 3-celled, cells 1-ovulate; fruit capsular 3-valved; seeds rugose\" (Stone, 1970. in PIER, 2002).
Notes
Widely planted as an ornamental, often in cemetaries (PIER, 2002). The sap may cause brief stinging and itching of the skin to some people, and when eaten, oysterplant will cause severe burning pain in the mouth and throat. Relatively tolerant of the allelopathic chemicals (compounds that prevent other plants from growing) put out by Australian pine (Floridata.com).
Uses
Primarily grown for bedding, rock gardens, and tropical effects. The reddening effect of the irritating juice has been used for cheek colouring also, (Floridata.com). The flower is used medicinally for the treatment of dysentery, enterorrhagia and hemoptysis (Brach).
Habitat Description
Prefers well-drained sites and will grow well on rocks (PIER, 2002). Although it likes soil with substantial organic matter, oysterplant will grow in sand or even coral rock (Floridata.com). It is drought resistant, Likes shade and will invade the forest understory (PIER, 2002).
Reproduction
T. spathacea can reproduce by seeds, cuttings, and discarded plants (PIER, 2002). Broken pieces will resprout easily (Floridata.com). Tradescantia spathacea flowers all year round, and is pollinated by insects, or self-pollinated (Center for Aquatic and Invasive Plants, 2000).
Principal source: Pacific Island Ecosystem at Risk (PIER),
Floridata.com L.C. Copyright 1996 - 2002
Compiler: IUCN/SSC Invasive Species Specialist Group (ISSG)
Review: Anon
Publication date: 2006-03-23
Recommended citation: Global Invasive Species Database (2026) Species profile: Tradescantia spathacea. Downloaded from http://www.iucngisd.org/gisd/species.php?sc=493 on 28-02-2026.
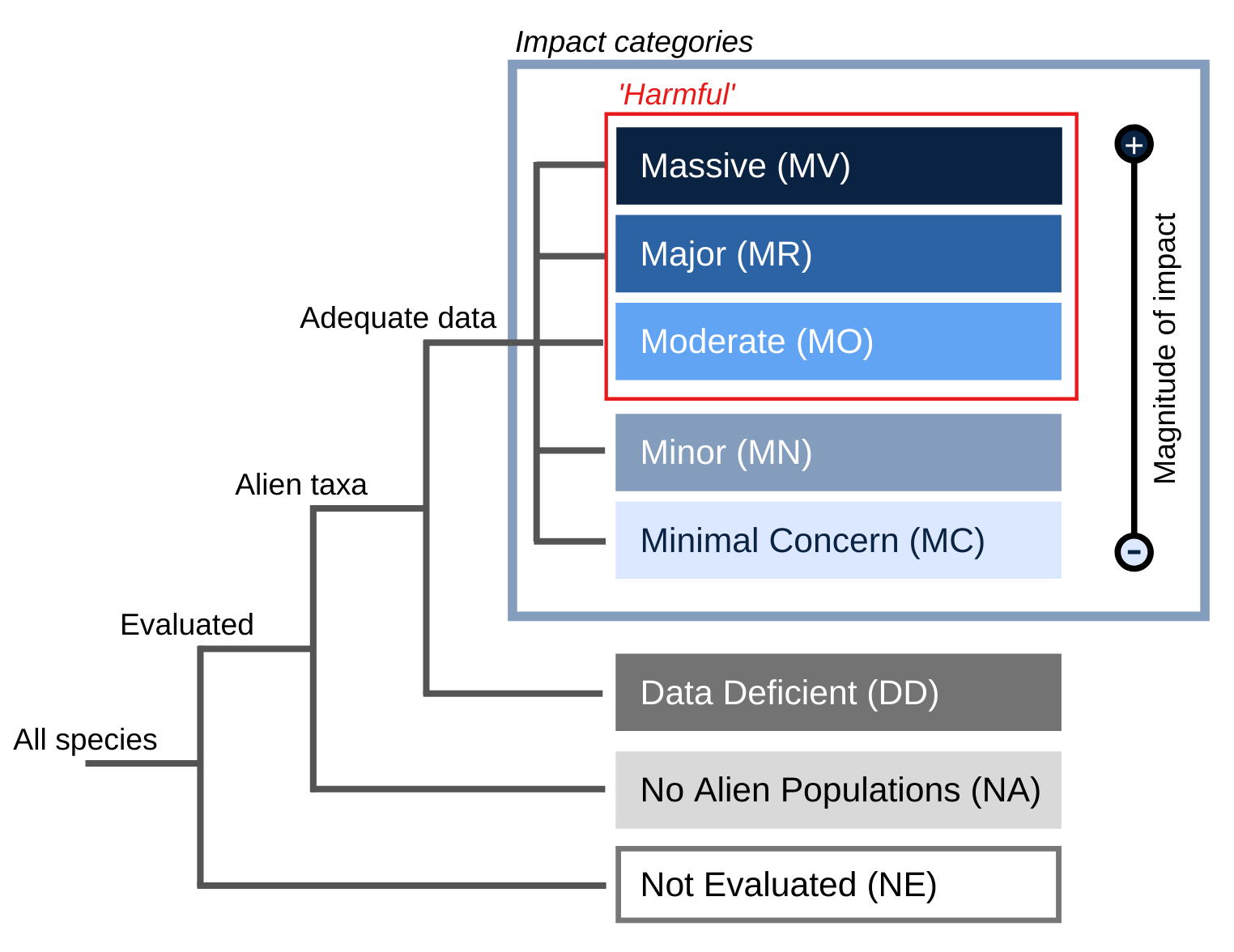
General Impacts
Can create a dense groundcover that prevents native plants from germinating on the forest floor. (Floridata.com)
Management Info
Preventative measures: Plant cuttings should not be dumped anywhere as this is a frequent source of new weed infestations. The origin of new top soil or fill should be checked as physical transportation of plant segments in soil is a major method of spread.