- General
- Distribution
- Impact
- Management
- Bibliography
- Contact
Emys holbrooki , Gray 1844
Emys sanguinolenta , Gray1855
Trachemys lineata , Gray 1873
Chrysemys scripta , var. elegans Boulenger 1889
Pseudemys scripta elegans , Stebbins 1985
Chrysemys scripta , (Boulenger 1889)
Pseudemys scripta , (Jordan 1899)
Testudo scripta , Schoepff, 1792
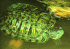
Eggs: The eggs are ovoid in shape, 31 to 43 millimeters long, 19 to 26 millimeters wide and weigh 6.1 to 15.4 grams (Bringsøe 2006).
Besides its distinctive red flashes the red-eared slider (like all turtles exotic to Australia) can also be identified by the way it retracts its head straight back into the shell; in comparison, all native Australian turtles wrap their heads around to the side of their shell (NRM&W).
In Europe, T. scripta elegans are generally released in freshwater areas which are frequented by humans such as public ponds which are considered of low biological value (e.g. Kordges 1990, Thiesmeier & Kordges 1990 1991, in Bringsøe 2006). Natural habitats close to urban areas are also used for releases (Bringsøe 2006). Natural reproduction of the red-eared slider in Europe under Mediterranean climate conditions has been reported (Luiselli et al. 1997, Martinez-Silvestre et al. 1997, Cadi et al. 2003, in Cadi & Joly 2003). The occurrence of the red-eared slider in a tropical urban polluted river in Brazil supports evidence of its capacity to use anthropogenic environments. Polluted rivers can offer a high amount of organic residues and food items, which can represent an advantage for such a generalist freshwater turtle species (Moll 1980, Lindeman 1996, Souza & Abe 2000, in Ferronato et al. 2009).\n
In its introduced range in Europe egg deposition has been observed in Spain (de Roa and Roig, 1997; Martinez-Silvestre, 1997; Bertolero and Canicio, 2000; Capalleras and Carretero, 2000, in Cadi et al. 2004), and near Paris, France (Moran Pers. Comm., in Cadi et al. 2004). However, sex determination of the Trachemys embryos is temperature-dependent, with cooler incubation temperatures producing only males, and warmer incubation temperatures only females (Ewert et al. 199, in Cadi et al. 2004). Therefore, incubation temperature could be a limiting factor for the invasion of this species in parts of Europe, if hatchlings of only one sex are produced in the wild (Cadi et al. 2004). A strong bias towards female red-eared sliders has been detected in capture sampling in France. This may reflect a potential strong female bias of imported juveniles; the incubation at high temperature leads to rapid hatching, but produces females in this species with temperature dependent sex determination (Godfrey et al. 2003, in Prévot-Julliard et al. 2007).
In northern Taiwan all feral T. scripta elegans sampled were found to have ingested animal materials (mostly snails, fish, adult and larval flies and unidentifiable terrestrial insects) and 76.5% were found to have ingested plant materials (Chen & Lue 1998, in Outerbridge 2008). Conversely Outerbridge (2008) found that only 77.8% of feral red-eared sliders examined in Bermuda had ingested animal materials whereas 86.1% had ingested plant materials. Most of the vegetative matter consisted of leaves, stalks, roots, seeds and flowers; however, filamentous and blue-green algae were also occasionally ingested. Nearly half of the animal material ingested comprised aquatic and terrestrial insects. Small fish, freshwater snails and bird remains occurred less frequently in the samples (Outerbridge 2008). \n
Prévot-Julliard et al. (2007) found fish remains in the stomachs of turtles. The size of fish scales found, some up to 12 mm in diameter, would have belonged to 20 cm fish (J.Y. Sire, Pers. Comm., in Prévot-Julliard et al. 2007). As it is unlikely that a slider turtle would be rapid enough to catch a 20 cm fish, perhaps the turtle acted as a necrophagous species, as other species of freshwater turtles do (Spencer et al. 1998, in Prévot-Julliard et al. 2007).\n
Prévot-Julliard et al. (2007) found four individuals which had ingested terrestrial ants, and one stomach was full of them. Although terrestrial activity is known for this species (Bennett et al. 1970, Gibbons 1970, in Prévot-Julliard et al. 2007), only few report are available for terrestrial foraging (Cagle 1944, Chen & Lue 1998, in Prévot-Julliard et al. 2007). The terrestrial activity of slider turtles is a key component for the colonisation of new habitat (Parker 1990, in Prévot-Julliard et al. 2007) making further investigation into this aspect of the turtle’s behavior warrented.
Principal source:
Compiler: IUCN SSC Invasive Species Specialist Group
Updates with support from the Overseas Territories Environmental Programme (OTEP) project XOT603, a joint project with the Cayman Islands Government - Department of Environment
Review: Paul Pendelbury, REPTRANS UK
Publication date: 2010-05-26
Recommended citation: Global Invasive Species Database (2026) Species profile: Trachemys scripta elegans. Downloaded from http://www.iucngisd.org/gisd/species.php?sc=71 on 10-03-2026.
Competition: The competitive advantages of the slider may include lower age at maturity, higher fecundity, and larger adult body size (Arvy & Servan 1998, in Cadi & Joly 2003). Turtles may compete for food, egg-laying sites, or basking places (Bury & Wolfheim 1973, Bury et al. 1979, Rovero et al. 1999, Lindeman 1999, in Cadi & Joly 2003). In a study by Cadi and Joly (2003), Emys were shown to shift their basking activity toward places considered to be of lower quality, while the dominant Trachemys occupied the better basking sites. Other studies have also shown red-eared sliders to compete with indigenous species for food and basking sites (Frank & McCoy 1995, Williams 1999, Salzberg 2000, in Somma & Fuller 2009). The red-eared slider has also been considered occasionally aggressive towards other individuals (Cadi & Joly 2003).\n
Threat to Endangered Species: Competitive interactions between T. scripta elegans and the European pond turtle (Emys orbicularis) are of particular interest, as the latter is registered as an endangered species (Appendix II of the Bern Convention, Corbett 1989, Luiselli et al. 1997, Martinez-Silvestre et al. 1997, in Cadi & Joly 2003, see Competition).\n
In Washington (USA) they are a potential threat to the Pacific pond turtle (Clemmys marmorata) a declining species endemic to the Pacific states (Brown et al. 1995, Williams 1999, in Somma & Fuller 2009). \n
Disease Transmission: Continuous releasing of exotic pet turtles in natural ecosystems increases the risk of parasite transmission to native species, and highlights the impending need for regulation of pet turtle trade in Europe (Hidalgo-Vila et al. 2008); the red-eared slider is known to carry nematodes (Hidalgo-Vila et al. 2008).\n
Predation: Turtles introduced near Paris were revealed to have consumed aquatic plants and animals (mostly arthropods and molluscs, Prévot-Julliard et al. 2007, in Teillac-Deschamps et al. 2008).\n
Human Health: Reptiles, including turtles, are well-recognised reservoirs for Salmonella, and are a source of human salmonellosis (Nagano et al. 2006). \n
Ecosystem Change: The impacts of T. scripta on natural habitats and ecosystems are unknown; should the red-eared slider be released in natural habitats with high ecological value, it would be relevant to monitor any consequences on native fauna and flora, typically invertebrates, amphibians, native turtles and nesting birds (Bringsøe 2006).
Preventative measures: With effect from 22 December 1997 the EU banned the import of the subspecies T. scripta elegans via the Protection of Species of Wild Fauna and Flora by Regulating Trade (Bringsøe 1998, 2001b, Bringsøe 2006). While it is no longer allowed to import the red-eared slider within the EU it is still legal to keep and distribute them within many EU countries.
After this legislation was passed the red-eared slider was semi-replaced in the market by other North American turtles which fetch higher prices and are imported in lower quantities (Adrados et al. 2002, in Bringsøe 2006). This may change if American turtle farmers manage to improve breeding success of these species in turtle farms. Unfortunately some of the species replacing the red-eared slider in the market are substantially better adapted to cold climates (such as Nova Scotia and Siberia, respectively) and probably represent a higher ecological risk; they are cryptic species and are significantly more carnivorous than the red-eared slider (P.P. van Dijk Pers. Comm. 2006).
Risk Assessment models for assessing the risk that exotic vertebrates could establish in Australia have been further explored by the Western Australia Department of Agriculture & Food (DAFWA) to confirm that they reasonably predict public safety, establishment and pest risks across a full range of exotic species and risk levels.
The Risk assessment for the Pond Slider (Trachemys scripta), has been assigned a VPC Threat Category of EXTREME.
Mammals and birds were assessed for the pest risk they pose if introduced to Australia, by calculating Vertebrate Pests Committee (VPC) Threat Categories. These categories incorporate risk of establishing populations in the wild, risk of causing public harm, and risk of becoming a pest (eg causing agricultural damage, competing with native fauna, etc). The 7-factor Australian Bird and Mammal Model was used for these assessments.
\r\nPhysical: Sliders can be captured by hand or through various trapping devices. Please visit Fyke Net for Turtles for information about turtle nets. Floating boards used by sliders as basking sites seem very effective when equipped with baited cages on top (Scalera 2006). Sniffer dogs can be used to detect and remove both turtles and their eggs; eggs can also be found and removed by following females at nesting areas (Scalera 2006).
In parts of Asia animals are released into the wild as a part of traditional Buddhist mercy ceremony to increase good karma, honour Buddha and repent for ones sins. The Ministry of the Environment (Republic of Korea ) advised that people should consider taking care of injured birds and animals and then set them free for a more environmentally-friendly symbolic act.
Knowledge and Research: The ecological effects of introductions of T. scripta elegans have been poorly documented (Platt & Fontenot 1992, in Ramsay et al. 2007). Competition of T. scripta elegans with the 'Lower Risk/Near Threatened (NT)' indigenous European pond turtle (see Emys orbicularis in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species) has been studied in France (see Cadi & Joly 2003). A French management project for the red-eared slider was initiated by the laboratory “Ecologie, Systématique and Evolution” (CNRS-University Paris-Sud) (Cadi et al. 2008).
- [1] asia
- [5] australia
- [1] austria
- [2] bahamas
- [1] bahrain
- [1] belgium
- [1] bermuda
- [1] brazil
- [1] cambodia
- [2] canada
- [1] cayman islands
- [1] chile
- [1] china
- [1] costa rica
- [1] czech republic
- [1] denmark
- [1] dominican republic
- [1] estonia
- [1] europe
- [1] faroe islands
- [1] finland
- [1] france
- [2] french polynesia
- [1] germany
- [1] gibraltar
- [1] greenland
- [4] guadeloupe
- [1] guam
- [1] guyana
- [1] hong kong
- [1] hungary
- [1] iceland
- [3] indonesia
- [1] israel
- [4] italy
- [2] japan
- [1] korea, democratic people's republic of
- [2] korea, republic of
- [1] latvia
- [1] lithuania
- [1] malaysia
- [1] martinique
- [2] micronesia, federated states of
- [1] new caledonia
- [1] new zealand
- [2] northern mariana islands
- [1] norway
- [1] panama
- [1] philippines
- [2] poland
- [5] puerto rico
- [1] reunion
- [1] saint lucia
- [1] singapore
- [1] south africa
- [3] spain
- [1] sri lanka
- [1] sweden
- [1] switzerland
- [1] taiwan
- [2] thailand
- [1] trinidad and tobago
- [1] united kingdom
- [5] united states
- [2] viet nam
- [2] virgin islands, british
- united states
| Location | Status | Invasiveness | Occurrence | Source |
 Mechanism:
Mechanism:  Outcome:
Outcome:  Ecosystem services:
Ecosystem services: Competition: The competitive advantages of the slider may include lower age at maturity, higher fecundity, and larger adult body size (Arvy & Servan 1998, in Cadi & Joly 2003). Turtles may compete for food, egg-laying sites, or basking places (Bury & Wolfheim 1973, Bury et al. 1979, Rovero et al. 1999, Lindeman 1999, in Cadi & Joly 2003). In a study by Cadi and Joly (2003), Emys were shown to shift their basking activity toward places considered to be of lower quality, while the dominant Trachemys occupied the better basking sites. Other studies have also shown red-eared sliders to compete with indigenous species for food and basking sites (Frank & McCoy 1995, Williams 1999, Salzberg 2000, in Somma & Fuller 2009). The red-eared slider has also been considered occasionally aggressive towards other individuals (Cadi & Joly 2003).\n
Threat to Endangered Species: Competitive interactions between T. scripta elegans and the European pond turtle (Emys orbicularis) are of particular interest, as the latter is registered as an endangered species (Appendix II of the Bern Convention, Corbett 1989, Luiselli et al. 1997, Martinez-Silvestre et al. 1997, in Cadi & Joly 2003, see Competition).\n
In Washington (USA) they are a potential threat to the Pacific pond turtle (Clemmys marmorata) a declining species endemic to the Pacific states (Brown et al. 1995, Williams 1999, in Somma & Fuller 2009). \n
Disease Transmission: Continuous releasing of exotic pet turtles in natural ecosystems increases the risk of parasite transmission to native species, and highlights the impending need for regulation of pet turtle trade in Europe (Hidalgo-Vila et al. 2008); the red-eared slider is known to carry nematodes (Hidalgo-Vila et al. 2008).\n
Predation: Turtles introduced near Paris were revealed to have consumed aquatic plants and animals (mostly arthropods and molluscs, Prévot-Julliard et al. 2007, in Teillac-Deschamps et al. 2008).\n
Human Health: Reptiles, including turtles, are well-recognised reservoirs for Salmonella, and are a source of human salmonellosis (Nagano et al. 2006). \n
Ecosystem Change: The impacts of T. scripta on natural habitats and ecosystems are unknown; should the red-eared slider be released in natural habitats with high ecological value, it would be relevant to monitor any consequences on native fauna and flora, typically invertebrates, amphibians, native turtles and nesting birds (Bringsøe 2006).

 Asia
Asia 
 AUSTRALIA
AUSTRALIA
 BERMUDA
BERMUDA
 BRAZIL
BRAZIL
 CANADA
CANADA
 CAYMAN ISLANDS
CAYMAN ISLANDS
 DOMINICAN REPUBLIC
DOMINICAN REPUBLIC
 FRANCE
FRANCE
 GERMANY
GERMANY
 ISRAEL
ISRAEL
 JAPAN
JAPAN
 LATVIA
LATVIA
 POLAND
POLAND
 PUERTO RICO
PUERTO RICO
 SINGAPORE
SINGAPORE
 SOUTH AFRICA
SOUTH AFRICA
 SPAIN
SPAIN
 TAIWAN
TAIWAN
 THAILAND
THAILAND
 UNITED STATES
UNITED STATES
 VIRGIN ISLANDS, BRITISH
VIRGIN ISLANDS, BRITISH
 Competition
Competition- Asia
- AUSTRALIA
- BERMUDA
- BRAZIL
- CANADA
- FRANCE
- GERMANY
- ISRAEL
- JAPAN
- LATVIA
- POLAND
- PUERTO RICO
- SINGAPORE
- SOUTH AFRICA
- SPAIN
- TAIWAN
- THAILAND
- UNITED STATES
- VIRGIN ISLANDS, BRITISH

 Predation
Predation- AUSTRALIA
- BERMUDA
- GERMANY
- JAPAN
- SINGAPORE
- UNITED STATES
- VIRGIN ISLANDS, BRITISH

 Hybridisation
Hybridisation- CAYMAN ISLANDS
- DOMINICAN REPUBLIC

 Disease transmission
Disease transmission- AUSTRALIA
- BRAZIL
- CANADA
- PUERTO RICO
- UNITED STATES

 Grazing/Herbivory/Browsing
Grazing/Herbivory/Browsing- TAIWAN

 Environmental Ecosystem - Habitat
Environmental Ecosystem - Habitat- [21] Reduction in native biodiversity

 Environmental Species - Population
Environmental Species - Population- [1] Species range change (i.e. contraction, shift)
- [2] Alteration of genetic resources
- [3] Plant/animal health

 Socio-Economic
Socio-Economic- [6] Human health
- [1] Other livelihoods
Preventative measures: With effect from 22 December 1997 the EU banned the import of the subspecies T. scripta elegans via the Protection of Species of Wild Fauna and Flora by Regulating Trade (Bringsøe 1998, 2001b, Bringsøe 2006). While it is no longer allowed to import the red-eared slider within the EU it is still legal to keep and distribute them within many EU countries.
After this legislation was passed the red-eared slider was semi-replaced in the market by other North American turtles which fetch higher prices and are imported in lower quantities (Adrados et al. 2002, in Bringsøe 2006). This may change if American turtle farmers manage to improve breeding success of these species in turtle farms. Unfortunately some of the species replacing the red-eared slider in the market are substantially better adapted to cold climates (such as Nova Scotia and Siberia, respectively) and probably represent a higher ecological risk; they are cryptic species and are significantly more carnivorous than the red-eared slider (P.P. van Dijk Pers. Comm. 2006).
Risk Assessment models for assessing the risk that exotic vertebrates could establish in Australia have been further explored by the Western Australia Department of Agriculture & Food (DAFWA) to confirm that they reasonably predict public safety, establishment and pest risks across a full range of exotic species and risk levels.
The Risk assessment for the Pond Slider (Trachemys scripta), has been assigned a VPC Threat Category of EXTREME.
Mammals and birds were assessed for the pest risk they pose if introduced to Australia, by calculating Vertebrate Pests Committee (VPC) Threat Categories. These categories incorporate risk of establishing populations in the wild, risk of causing public harm, and risk of becoming a pest (eg causing agricultural damage, competing with native fauna, etc). The 7-factor Australian Bird and Mammal Model was used for these assessments.
\r\nPhysical: Sliders can be captured by hand or through various trapping devices. Please visit Fyke Net for Turtles for information about turtle nets. Floating boards used by sliders as basking sites seem very effective when equipped with baited cages on top (Scalera 2006). Sniffer dogs can be used to detect and remove both turtles and their eggs; eggs can also be found and removed by following females at nesting areas (Scalera 2006).
In parts of Asia animals are released into the wild as a part of traditional Buddhist mercy ceremony to increase good karma, honour Buddha and repent for ones sins. The Ministry of the Environment (Republic of Korea ) advised that people should consider taking care of injured birds and animals and then set them free for a more environmentally-friendly symbolic act.
Knowledge and Research: The ecological effects of introductions of T. scripta elegans have been poorly documented (Platt & Fontenot 1992, in Ramsay et al. 2007). Competition of T. scripta elegans with the 'Lower Risk/Near Threatened (NT)' indigenous European pond turtle (see Emys orbicularis in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species) has been studied in France (see Cadi & Joly 2003). A French management project for the red-eared slider was initiated by the laboratory “Ecologie, Systématique and Evolution” (CNRS-University Paris-Sud) (Cadi et al. 2008).

 AUSTRALIA
AUSTRALIA
 AUSTRIA
AUSTRIA
 BELGIUM
BELGIUM
 BERMUDA
BERMUDA
 BRAZIL
BRAZIL
 CHINA
CHINA
 FRANCE
FRANCE
 GUADELOUPE
GUADELOUPE
 GUAM
GUAM
 ISRAEL
ISRAEL
 ITALY
ITALY
 JAPAN
JAPAN
 KOREA, REPUBLIC OF
KOREA, REPUBLIC OF
 LATVIA
LATVIA
 MARTINIQUE
MARTINIQUE
 MICRONESIA, FEDERATED STATES OF
MICRONESIA, FEDERATED STATES OF
 NEW ZEALAND
NEW ZEALAND
 POLAND
POLAND
 PUERTO RICO
PUERTO RICO
 REUNION
REUNION
 SINGAPORE
SINGAPORE
 SPAIN
SPAIN
 SWITZERLAND
SWITZERLAND
 TAIWAN
TAIWAN
 THAILAND
THAILAND
 UNITED KINGDOM
UNITED KINGDOM
 UNITED STATES
UNITED STATES
 VIET NAM
VIET NAM
 VIRGIN ISLANDS, BRITISH
VIRGIN ISLANDS, BRITISH


 Prevention
Prevention- AUSTRALIA
- AUSTRIA
- BELGIUM
- BERMUDA
- BRAZIL
- CHINA
- FRANCE
- GUADELOUPE
- GUAM
- ISRAEL
- JAPAN
- KOREA, REPUBLIC OF
- LATVIA
- MARTINIQUE
- MICRONESIA, FEDERATED STATES OF
- REUNION
- SINGAPORE
- TAIWAN
- UNITED KINGDOM
- UNITED STATES

 Control
Control- ITALY
- POLAND
- SPAIN
- SWITZERLAND
- UNITED STATES

 None
None
 Unknown
Unknown- GUADELOUPE
- MARTINIQUE
- PUERTO RICO
- REUNION
- VIRGIN ISLANDS, BRITISH

 Monitoring
Monitoring- FRANCE
- NEW ZEALAND
- VIET NAM
Management information
Summary: Report from Costa Rica.
Summary: Reports of Trachemys scripta elegans in Italy.
Summary: Interesting and timely information on invasive species and associated issues. Focuses on conservation issues and includes news of upcoming conferences, publications, and reports.
Summary: Available from: http://www.issg.org/pdf/aliens_newsletters/A19-20.pdf [Accessed 12 March 2003]
Summary: Available from: http://www.feral.org.au/wp-content/uploads/2010/03/PC12803.pdf [Accessed August 19 2010]
Summary: Available from: http://www.victoria.ac.nz/srarnz/files/Gatrell_Kirk_Euthanasia_Reptiles.pdf [Accessed 28 December 2009]
Summary: The North European and Baltic Network on Invasive Alien Species (NOBANIS) is a gateway to information on alien and invasive species in North and Central Europe. The participating countries are Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Faroe Islands, Germany, Greenland, Iceland, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Poland, European part of Russia, Sweden. The NOBANIS project will provide fact sheets on 60 of the most invasive alien species of the region, covering both animals and plant as well as microorganisms. We intend to upload 60 fact sheets - so please visit this page regularly.
NOBANIS is available from: www.nobanis.org, this page is available from: http://www.nobanis.org/files/factsheets/Trachemys_scripta.pdf [Accessed 31 October 2006]
Summary: Available from: http://www.herpetologica.org/revista/rev22/Resumen11%20CADI%20ET%20AL%20segundo.pdf [Accessed 28 December 2009]
Summary: Report from Taiwan.
Summary: Available from: http://data.iucn.org/dbtw-wpd/edocs/2006-061.pdf#page=196 [Accessed 28 December 2009]
Summary: Available from: http://www.europe-aliens.org/speciesFactsheet.do?speciesId=50003 [Accessed 28 December 2009]
Summary: Available from: http://www.freewebs.com/trachemysadoption/articles/DaSilvaBlasco.pdf [Accessed 18 January 2009]
Summary: A survey of abandons of Trachemys scripta elegans in several reception centres in 2004 shows a decrease of abandons since the ban in the European Union.
Summary: To obtain reliable data on the current situation of Emys orbicularis in the Salentine peninsula (Salento, South Apulia, Italy), 15 wetlands along the Adriatic and Ionic coasts were surveyed. E. orbicularis was recorded in 13 sites. However, reproduction was confirmed only for six populations. A particular cause of concern is the presence of reproducing red-eared sliders (T. scripta elegans) at three sites.
Summary: Reports of Trachemys scripta elegans in Italy.
Summary: In Metropolitan France, 36 regularly breeding amphibians and 33 regularly breeding reptiles are presently recorded. The red-eared turtle (Trachemys scripta elegans) may be naturalised in the near future.
Summary: The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species provides taxonomic, conservation status and distribution information on taxa that have been globally evaluated using the IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria. This system is designed to determine the relative risk of extinction, and the main purpose of the IUCN Red List is to catalogue and highlight those taxa that are facing a higher risk of global extinction (i.e. those listed as Critically Endangered, Endangered and Vulnerable). The IUCN Red List also includes information on taxa that are categorized as Extinct or Extinct in the Wild; on taxa that cannot be evaluated because of insufficient information (i.e. are Data Deficient); and on taxa that are either close to meeting the threatened thresholds or that would be threatened were it not for an ongoing taxon-specific conservation programme (i.e. are Near Threatened).
Available from: http://www.iucnredlist.org/ [Accessed 25 May 2011]
Summary: This compilation of information sources can be sorted on keywords for example: Baits & Lures, Non Target Species, Eradication, Monitoring, Risk Assessment, Weeds, Herbicides etc. This compilation is at present in Excel format, this will be web-enabled as a searchable database shortly. This version of the database has been developed by the IUCN SSC ISSG as part of an Overseas Territories Environmental Programme funded project XOT603 in partnership with the Cayman Islands Government - Department of Environment. The compilation is a work under progress, the ISSG will manage, maintain and enhance the database with current and newly published information, reports, journal articles etc.
Summary: Models for assessing the risk that exotic vertebrates could establish in Australia have been developed for mammals, birds (Bomford 2003; Bomford 2006, 2008), reptiles and amphibians (Bomford 2006, 2008; Bomford et al. 2005). These Risk Assessment models have been further explored by Western Australia Department of Agriculture & Food (DAFWA) to confirm that they reasonably predict public safety, establishment and pest risks across a full range of exotic species and risk levels. Mammals and birds were assessed for the pest risk they pose if introduced to Australia, by calculating Vertebrate Pests Committee (VPC) Threat Categories. These categories incorporate risk of establishing populations in the wild, risk of causing public harm, and risk of becoming a pest (eg causing agricultural damage, competing with native fauna, etc). The 7-factor Australian Bird and Mammal Model was used for these assessments.
Summary: Available from: http://herp-or.uv.ro/nwjz/content/v5.1/nwjz.051105.Kitowski.pdf [Accessed 28 December 2009]
Summary: This report documents work contributing to a project commissioned by the Invasive Animals Cooperative Research Centre to validate and refine risk assessment models used in decisions to import and manage introduced vertebrate species. The intent of the project was to: a) increase predictive accuracy, scientific validation and adoption of risk assessment models for the import and keeping of exotic vertebrates, and b) reduce the risk of new vertebrate pests establishing introduced populations in Australia.
Available from: http://www.feral.org.au/wp-content/uploads/2010/08/DAFWA_RA_060510.pdf [Accessed 16 March 2011]
Summary: Spread of Trachemys scripta elegans in Poland.
Summary: This chapter reviews what is currently known about the status of red-eared sliders in Asia, as well as the potential impact of this non-indigenous species on the native Asian biota. It includes published literature, information from websites, as well as mentioning ongoing research where known.
Summary: Red-eared slider population monitoring.
Summary: Available from: http://www.dpi.qld.gov.au/4790_8289.htm [Accessed 18 January 2009]
Summary: Report from Republic of Korea.
Summary: Report from Republic of Korea.
Summary: Available from: http://www.europe-aliens.org/pdf/Trachemys_scripta.pdf [Accessed 28 December 2009]
Summary: Report from France.
Summary: Available from: http://www2.mnhn.fr/cersp/IMG/pdf/Tiellac_al-HerpetologicalConservation-2008.pdf [Accessed 28 December 2009]
Summary: Report from Republic of Korea.
Summary: Up to 16 species of native turtles still inhabit the Mae Klong basin and adjacent minor drainages; among these are several rare species; the high number of genera (10 to 15) may make it the world s most diverse turtle community (Thirakhupt & Van Dijk 1994). Exotic turtle species, specifically the chinese softshell (Pelodiscus sinensis) and the red-eared terrapin (Trachemys scripta elegans) were introduced to Thailand in recent years. The exotic turtle species present in Mae Klong basin have a proven potential to disrupt native turtle populations. Their establishment in the wild should be prevented.
Summary: This database compiles information on alien species from British Overseas Territories.
Available from: http://www.jncc.gov.uk/page-3660 [Accessed 10 November 2009]
Summary: Report from Viet Nam.
Summary: Craig Walton. Principal Project Officer, Queensland Interagency Pest Management Committee.
Summary: This paper outlines alien freshwater turtles which may become established in Japan in the near future. The following turtles designated by the law for the protection of indigenous ecology are discussed: Macroclemys temmincki, Apalone spp., Graptemys spp., Pseudemys spp. Trachemys scripta scripta and Ocadia sinensis. Trachemys scripta elegans and Polodiscus sinensis sinensis are already established in Japan.
Summary: Abstract: The North American species of turtle Trachemys scripta has been introduced into the Czech Republic. First records of the pond slider are from the 60�s.We have put together a list of 190 records of the pond slider in the Czech Republic, on the basis of published data, verbal notices and unpublished data. In 9 cases we have noted a count of 10 and more specimens.The main areas of occurrence are regions with warmer climate: Prague and surroundings, Polab� (along Elbe river), north Moravia (Opava and Ostrava regions) and some localities in south Moravia. 4 attempts of reproduction were noted. In one case the eggs were succesfully artificially incubated for the period of 95 days at 25,5�C.
Summary: Ce livre propose une synth�se sur les amphibiens et reptiles terrestres de l archipel Guadeloup�en. Six esp�ces d anoures, 5 de tortues, 21 de l�zards dont 4 �teintes et 7 de serpents sont d�taill�es.
Summary: Available from: http://www.wildlifebc.org/UserFiles/File/2_2_Bunnell.pdf [Accessed 28 December 2009]
Summary: Shelley (2007) investigated whether exotic turtle species were capable of establishing breeding populations in the Sydney area and confirmed that two exotic species were present: Trachemys scripto elegans and Clemmys marmorato.
Summary: English:
The species list sheet for the Mexican information system on invasive species currently provides information related to Scientific names, family, group and common names, as well as habitat, status of invasion in Mexico, pathways of introduction and links to other specialised websites. Some of the higher risk species already have a direct link to the alert page. It is important to notice that these lists are constantly being updated, please refer to the main page (http://www.conabio.gob.mx/invasoras/index.php/Portada), under the section Novedades for information on updates.
Invasive species - reptiles is available from: http://www.conabio.gob.mx/invasoras/index.php/Especies_invasoras_-_Reptiles [Accessed 30 July 2008]
Spanish:
La lista de especies del Sistema de informaci�n sobre especies invasoras de m�xico cuenta actualmente con informaci�n aceca de nombre cient�fico, familia, grupo y nombre com�n, as� como h�bitat, estado de la invasi�n en M�xico, rutas de introducci�n y ligas a otros sitios especializados. Algunas de las especies de mayor riesgo ya tienen una liga directa a la p�gina de alertas. Es importante resaltar que estas listas se encuentran en constante proceso de actualizaci�n, por favor consulte la portada (http://www.conabio.gob.mx/invasoras/index.php/Portada), en la secci�n novedades, para conocer los cambios.
Especies invasoras - Reptiles is available from: http://www.conabio.gob.mx/invasoras/index.php/Especies_invasoras_-_Reptiles [Accessed 30 July 2008]
Summary: Notes on red-eared slider in Brazil and salmonella.
Summary: No abstract
Summary: During ecological studies carried out on some introduced populations of Trachemys scripta elegans, for the first time egg-laying patterns and reproductive success has been recorded in semi-natural habitats of Lombardy.
Summary: Available from: http://data.gbif.org/species/14835399 [Accessed 15 June 2010]
Summary: Available from: http://nis.gsmfc.org/nis_factsheet.php?toc_id=208 [Accessed 28 December 2009]
Summary: Trachemys scripta elegans is recorded in Chile. It is discussed as a possible invading species in Chile s mediterraean zone.
Summary: Twelve species form the native herpetofauna of Maiao Island, Society Archipelago (French Polynesia). Two geckos (Hemidactylus frenatus and Phelsuma laticauda) have been recently introduced and T. scripta elegans was introduced about 15 years ago (Ineich 2009).
Summary: An online database that provides taxonomic information, common names, synonyms and geographical jurisdiction of a species. In addition links are provided to retrieve biological records and collection information from the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) Data Portal and bioscience articles from BioOne journals.
Available from: http://www.cbif.gc.ca/pls/itisca/taxastep?king=every&p_action=containing&taxa=Trachemys+scripta+elegans&p_format=&p_ifx=plglt&p_lang= [Accessed March 2005]
Summary: The distribution of all 25 turtle species recorded from Florida are mapped and reviewed.
Summary: Distribution pattern of freshwater turtles was investigated along the Koito River basin, Boso Peninsula, central Japan.
Summary: The number of exotic species of reptiles and amphibians introduced to the Bahamas continues to grow. Lee (2005) reviews the documented introductions and reports on four additional species.
Summary: Cet article fait le point des connaissances sur les amphibiens et les reptiles indig�nes et introduits des Antilles fran�aises. Les impacts des esp�ces introduites sur la faune indig�ne sont discut�s. Le cas de la conservation des populations d Iguana delicatissima sur l�le de Petite-Terre est pr�sent�
Summary: This paper reports on an investigation designed to survey a mixed population of Emys orbicularis and Trachemys scripta elegans in the Moulin-de-Vert reserve (Canton of Geneva, SW Switzerland) 50 years after introduction of the first E. orbicularis, and to study the habitat use by E. orbicularis there. The authors estimate the population size to be 306 +/- 10.5 turtles. This corresponds to a density of 64 individuals per hectare.
Summary: Available from: http://www.nobanis.org/speciesInfo.asp?taxaID=713 [Accessed 27 December 2009]
Summary: Available from: http://www.airies.or.jp/publication/ger/pdf/08-02-04.pdf [Accessed 28 December 2009]
Summary: Synth�se des introductions d esp�ces de vert�br�s en Nouvelle-Cal�donie et �valuation de leurs impacts.
Summary: In 2001 an intensive herpetofaunal mapping project was launched to build a detailed database for Hungary. Using different sampling methods, Emys orbicularis was found in semi-natural lentic and lotic waters as well as in canals, fishponds and other artificial water bodies. Both natural and anthropogenic factors endanger E. Orbicularis causing local extinctions, e. g., through habitat destruction, fragmentation, drought, and isolation. Sporadic records of Trachemys scripta elegans in the wild are known as well but no evidence has been collected on its reproduction so far. E. Orbicularis has the potential to become not only a keystone species in biological monitoring but also a symbol of wetland conservation.
Summary: Available from: http://biologs.bf.lu.lv/grozs/LU/LU_Bio_Raksti/LUBioRaksti/2007/Pupins.pdf [Accessed 28 December 2009]
Summary: Available from: http://reptile-database.reptarium.cz/species.php?genus=Trachemys&species=scripta [Accessed September 8 2010]
Summary: T. scripta elegans, an invasive species introduced by pet trade to fresh water bodies nearly all over the world, has recently been listed for Sulawesi.
Summary: Examples of turtles (mainly Emys orbicularis and Testudo hermanni hermanni) reintroductions and introductions (Trachemys scripta elegans) in France are analysed.
Summary: Since 1999, introduced Trachemys scripta elegans from artificial and natural water bodies in the Po plain (North Italy) were bacteriologically screened. From 2001 onwards, a survey of Emys orbicularis was started in the same area. 15 carcasses and 349 cloacal swabs from T. scripta elegans, and 100 cloacal swabs from E. Orbicularis have been studied. Most samples yielded positive bacteriological results. Bacteria known as pathogens for chelonians (eg: Aeromonas hydrophila, Citrobacter freundii, Pseudomonas spp., Edwardsiella tarda), have been identified.
Summary: Available from: http://nas.er.usgs.gov/queries/FactSheet.asp?speciesID=1261 [Accessed 28 December 2009]
Summary: Available from: http://tucsonherpsociety.org/Stitt%202005_18(6)65.pdf [Accessed 28 December 2009]
Summary: Recent field work and a review of catalogued specimens in the herpetology collections at the Yale Peabody has yielded 170 new town records for amphibians and reptiles in Connecticut. These are reported here, along with observations on the status of the red-ear slider (Trachemys scripta elegans) in Connecticut.
Summary: Study on red-eared slider in Florida
Jean-Fran�ois
Ecosystem: Terrestrial
Paul
Studying the impacts of invasives, frog decline and impacts of effemeralism of water-courses on amphibians. A specialist in the catching and transporting of protected species of Reptiles and Amphibians
red-eared slider, punakorvakilpikonna, red-eared slider terrapin, sarkanausu brunurupucis, Rotwangen-Schmuckschildkroete, Krasnoukhaya cherepakha, Rotwangen-Schmuckschildkr�te , punakõrv-ilukilpkonn, raudonausis vežlys , rödörad vattensköldpadda, rødøreterrapin, rødøret terrapin, zólw czerwonolicy, zólw czerwonouchy, zólw ozdobny, Nordamerikansk terrapin, slider, Buchstaben-Schmuckschildkröte, raudonskruostis vežlys