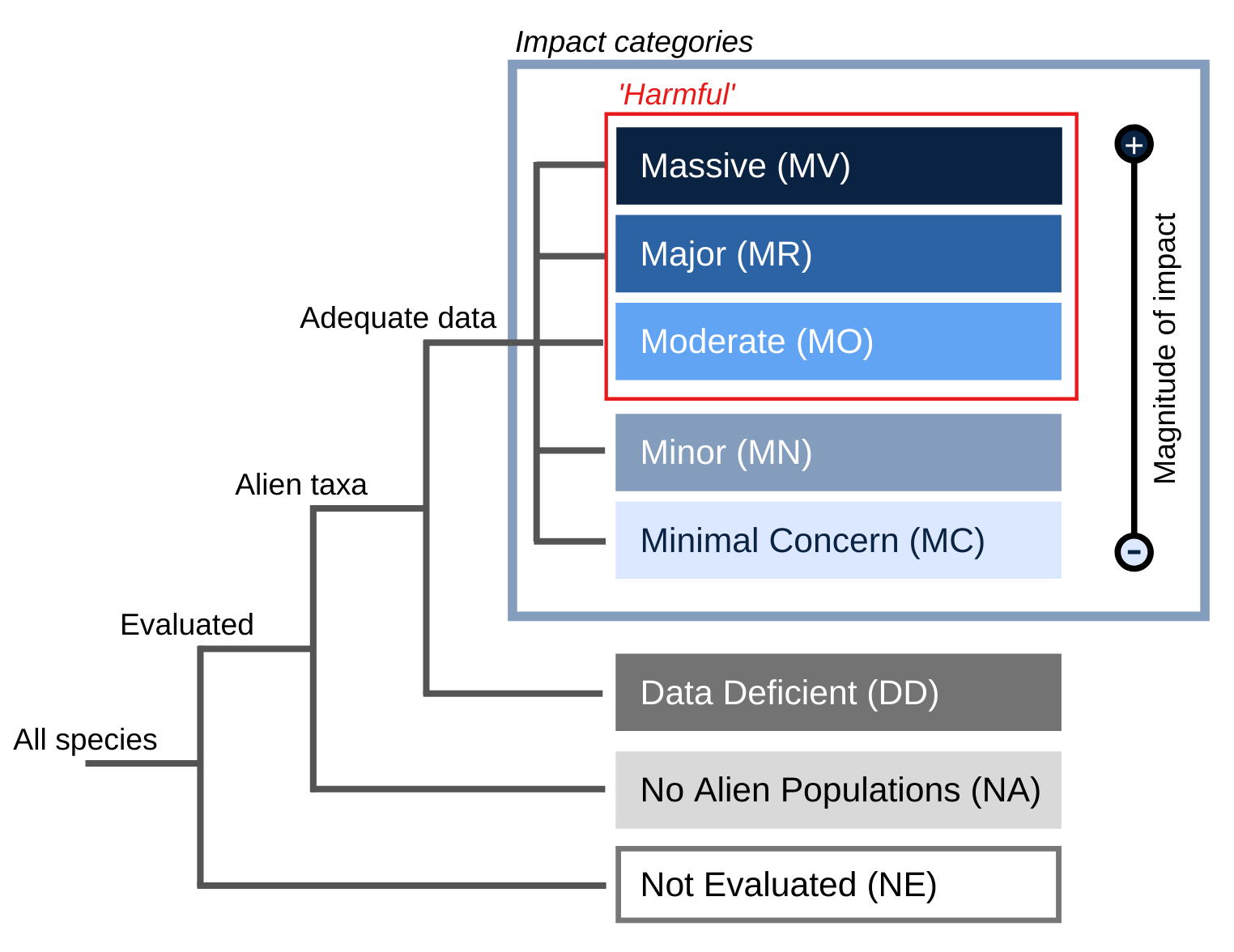
- Not Evaluated
NE - No Alien Population
NA - Data Deficient
DD - Minimal Concern
MC - Minor
MN - Moderate
MO - Major
MR - Massive
MV
- General
- Distribution
- Impact
- Management
- Bibliography
- Contact
A. decurrens , var. mollis
Principal source: Pacific Island Ecosystems At Risk (PIER), 2010. Acacia mearnsii
Compiler: IUCN SSC Invasive Species Specialist Group
Updates with support from the Overseas Territories Environmental Programme (OTEP) project XOT603, a joint project with the Cayman Islands Government - Department of Environment
Review: Dr. Hélia Marchante. Escola Superior Agrária de Coimbra Departamento de Ciências Exactas e Ambiente Sector de Biologia e Ecologia, Bencanta. 3040-316 Coimbra Portugal.
Publication date: 2010-10-04
Recommended citation: Global Invasive Species Database (2026) Species profile: Acacia mearnsii. Downloaded from http://www.iucngisd.org/gisd/species.php?sc=51 on 15-02-2026.
Commercial plantations and invasive stands of A .mearnsii in South Africa reduce surface runoff and decrease water ability, causing an estimated annual economic loss of $US 2.8 million. According to KwaZulu-Natal Wildlife (the governmental agency responsible for managing protected areas in KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa) the advance of \nalien plants (particularly Chromolaena odorata, Lantana camara, Acacia dealbata, and Acacia mearnsii) is the most significant past and future threat to conservation in these areas (De Wit, Crookes and Van Wilgen, 2001; Goodman, 2003)
Integrated management: The Working for Water programme implemented by the South African Government is a collaborative program that aims to ameliorate the problems caused by Acacia species and other invasive plants. The program consists of more than 30 sub-projects in eight provinces in the country and consists of the clearing of weeds from water courses (by mechanical and chemical methods). Between 1995 and 2000 over $100 million of poverty-relief funds on the program which was labour intensive and provided job opportunities for local communities. After seven years of implementation of the project it became clear that rehabilitation of sites (following the removal of alien plant species) would sometimes be needed in order to prevent or reduce the soil erosion stimulated by the clearing of plants (Van Wilgen et al., 2002, Milton, Dean and Richardson, 2003).
Richardson & Kluge (2008) observe that preventing the accumulation of seed banks by reducing seed production is critical to all successful management programmes and that biological control is the most effective and practical option.
Please follow this link for more details on Chemical and Biological control options that have been found promising and effective.
- [1] algeria
- [1] china
- [1] cook islands
- [1] france
- [2] india
- [1] israel
- [1] italy
- [1] japan
- [1] madagascar
- [2] new zealand
- [12] portugal
- [1] reunion
- [1] saint helena
- [1] seychelles
- [10] south africa
- [1] spain
- [1] swaziland
- [1] taiwan
- [1] tanzania, united republic of
- [1] uganda
- [1] united states
- [1] zimbabwe
- australia
| Location | Status | Invasiveness | Occurrence | Source |
 Mechanism:
Mechanism:  Outcome:
Outcome:  Ecosystem services:
Ecosystem services: Commercial plantations and invasive stands of A .mearnsii in South Africa reduce surface runoff and decrease water ability, causing an estimated annual economic loss of $US 2.8 million. According to KwaZulu-Natal Wildlife (the governmental agency responsible for managing protected areas in KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa) the advance of \nalien plants (particularly Chromolaena odorata, Lantana camara, Acacia dealbata, and Acacia mearnsii) is the most significant past and future threat to conservation in these areas (De Wit, Crookes and Van Wilgen, 2001; Goodman, 2003)
- Aeshna subpupillata LC
- Allocnemis leucosticta LC
- Anax imperator mauritianus LC
- Anax speratus LC
- Anthoxanthum borii NT
- Antirhea borbonica LC
- Aphloia theiformis LC
- Brachylaena discolor LC
- Carissa edulis LC
- Ceratogomphus pictus LC
- Ceriagrion glabrum LC
- Chlorolestes apricans EN
- Chlorolestes umbratus LC
- Combretum kraussii LC
- Crocothemis sanguinolenta LC
- Cyperus rotundus LC
- Diospyros lycioides LC
- Dombeya rotundifolia LC
- Elattoneura frenulata LC
- Elattoneura glauca LC
- Euclea natalensis LC
- Heteromirafra ruddi VU
- Metacnemis angusta VU
- Metacnemis valida EN
- Nuxia floribunda LC
- Olea lancea LC
- Orthetrum julia capicola LC
- Palpopleura jucunda LC
- Paragomphus cognatus LC
- Pittosporum senacia LC
- Platycypha fitzsimonsi LC
- Pseudagrion draconis LC
- Pseudagrion furcigerum LC
- Pseudagrion kersteni LC
- Rhus pentheri LC
- Setaria sphacelata LC
- Tramea limbata LC
- Trithemis arteriosa LC
- Trithemis dorsalis LC
- Trithemis furva LC
- Trithemis stictica LC
- Vachellia karroo LC
- Zanthoxylum capense LC
- Ziziphus mucronata LC
- Zygonyx natalensis LC

 ALGERIA
ALGERIA
 INDIA
INDIA
 ISRAEL
ISRAEL
 REUNION
REUNION
 SOUTH AFRICA
SOUTH AFRICA
 UGANDA
UGANDA
 Competition
Competition- INDIA
- ISRAEL
- REUNION
- SOUTH AFRICA

 Poisoning/Toxicity
Poisoning/Toxicity- ALGERIA
- REUNION
- SOUTH AFRICA

 Flammability
Flammability- SOUTH AFRICA

 Other
Other
 Environmental Ecosystem - Habitat
Environmental Ecosystem - Habitat- [1] Modification of hydrology/water regulation, purification and quality /soil moisture
- [2] Modification of nutrient pool and fluxes
- [5] Reduction in native biodiversity
- [1] Habitat degradation
- [1] Modification of fire regime
- [1] Modification of successional patterns
- [1] Soil or sediment modification: erosion

 Socio-Economic
Socio-Economic- [1] Damage to agriculture
- [1] Alteration of recreational use and tourism
- [1] Limited access to water, land and other
- [1] Other economic impact
- [1] Other livelihoods
Integrated management: The Working for Water programme implemented by the South African Government is a collaborative program that aims to ameliorate the problems caused by Acacia species and other invasive plants. The program consists of more than 30 sub-projects in eight provinces in the country and consists of the clearing of weeds from water courses (by mechanical and chemical methods). Between 1995 and 2000 over $100 million of poverty-relief funds on the program which was labour intensive and provided job opportunities for local communities. After seven years of implementation of the project it became clear that rehabilitation of sites (following the removal of alien plant species) would sometimes be needed in order to prevent or reduce the soil erosion stimulated by the clearing of plants (Van Wilgen et al., 2002, Milton, Dean and Richardson, 2003).
Richardson & Kluge (2008) observe that preventing the accumulation of seed banks by reducing seed production is critical to all successful management programmes and that biological control is the most effective and practical option.
Please follow this link for more details on Chemical and Biological control options that have been found promising and effective.

 AUSTRALIA
AUSTRALIA
 PORTUGAL
PORTUGAL
 SOUTH AFRICA
SOUTH AFRICA
 UNITED STATES
UNITED STATES
 Prevention
Prevention- PORTUGAL
- UNITED STATES

 Control
Control- AUSTRALIA
- SOUTH AFRICA
Management information
Summary: Information on the effects of A. mearnsii in South Africa and possible biological control agents.
Summary: A study on the use of a screening system to assess proposed plant introductions to Hawaii or other Pacific Islands and to identify high-risk species used in horticulture and forestry which would greatly reduce future pest-plant problems and allow entry of most nonpests.
Summary: A good overview of the associated uses and negative impacts of A. mearnsii in South Africa, as well
Summary: A study on the evaporation rates from areas infested with A. mearnsii in Western Cape and KwaZulu-Natal in South Africa.
Summary: The threats to conservation faced in the KwaZulu-Natal province of South Africa.
Summary: The paper discusses the appropriateness of the wasp Bruchophagus acaciae for use as a biological control agent for Australian Acacia species.
Summary: This compilation of information sources can be sorted on keywords for example: Baits & Lures, Non Target Species, Eradication, Monitoring, Risk Assessment, Weeds, Herbicides etc. This compilation is at present in Excel format, this will be web-enabled as a searchable database shortly. This version of the database has been developed by the IUCN SSC ISSG as part of an Overseas Territories Environmental Programme funded project XOT603 in partnership with the Cayman Islands Government - Department of Environment. The compilation is a work under progress, the ISSG will manage, maintain and enhance the database with current and newly published information, reports, journal articles etc.
Summary: Data published to assist applicators experimenting with herbicides for weed control.
Summary: Ecology, synonyms, common names, distributions (Pacific as well as global), management and impact information
Available from: http://www.hear.org/pier/species/acacia_mearnsii.htm [Accessed 17 June 2003]
Summary: A database of Swaziland s alien plant species.
Summary: This database compiles information on alien species from British Overseas Territories.
Available from: http://www.jncc.gov.uk/page-3660 [Accessed 10 November 2009]
Summary: Information on the distribution and effects of A. mearnsii on Reunion Island.
Summary: Rates A. mearnsii as a scattered, or local, weed.
Summary: Brief information on Acacia mearnsii in Hawaii.
Available from: http://www.botany.hawaii.edu/faculty/carr/aca_mea.htm [Accessed 18 June 2003]
Summary: Base de données sur la flore de la Réunion. De nombreuses informations tres utiles.
Available from: http://flore.cbnm.org/index2.php?page=taxon&num=a684eceee76fc522773286a895bc8436 [Accessed 28 March 2008]
Summary: Brief summary of features of Acacia mearnsii primarily with an African perspective.
Available from: http://www.hort.purdue.edu/newcrop/duke_energy/Acacia_mearnsii.html [Accessed 17 June 2003]
Summary: Dendrology book of species present in Portugal
Summary: Portuguese Flora
Summary: Plant Protection Research Institute Handbook No. 5
Summary: An online database that provides taxonomic information, common names, synonyms and geographical jurisdiction of a species. In addition links are provided to retrieve biological records and collection information from the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) Data Portal and bioscience articles from BioOne journals.
Available from: http://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=182081 [Accessed December 31 2004]
Summary: Available from: http://www.fao.org/forestry/webview/media?mediaId=6842&langId=2 [Accessed 26 March 2008]
Summary: A study on the regeneration levels in areas invaded by exotic plants in the Mgahinga Gorilla National Park (MGNP), Uganda.
Summary: Interactions between vegetation and groundwater including interception, root uptake, transpiration and other factors.
Summary: Cet article est le premier à proposer une hiérarchisation des plantes les plus envahissantes de La Réunion. 33 plantes ont été ainsi classées en utilisant une méthode développée en Afrique du Sud. Les bases d une stratégie de lutte contre les plantes exotiques envahissantes sont également formulées.
Summary: Resource that includes the distribution of invasive species throughout the Pacific Islands.
Summary: Proposed benefits of some land use strategies in South Africa (including game hunting).
Summary: Flora of Iberian Peninsula
Summary: Mentions that invertebrate species richness and diversity are affected by A. mearnsii.
Summary: Cet article propose un bilan des methodes et des resultats relatifs aux etudes traitant de la connaissance des consequences ecologiques des invasions de plantes exotiques.
Summary: L'inventaire de 318 especes de plantes ligneuses introduites à la Réunion, permet d en identifier 132 comme naturalisees dans les ecosystemes naturels. 26 de ces especes choisies parmi les plus envahissantes ont été classees en fonction de leur impact biologique sur les ecosystemes indigenes.
Summary: Discussion about some physical processes that are disrupted by alien plant species.
Summary: European Flora
Summary: An overview of the soil improving properties of some trees and a list of soil improving species.
Available from: http://www.nofa.org/tnf/sp02/supplement/effects.pdf [Accessed 23 December 2004]
Prof. Adjunta Hélia
Webpage
Jacques
Ecosystem: Terrestrial
Julien
Ecosystem: Terrestrial
Australische akazie, uwatela, Australian acacia, swartwattel, black wattle, acácia-negra
A. mearnsii caused a decline in grass species diversity and richness, but it returned after restoration took place (Vundla, 2018). A. mearnsii invasion reduced bacterial diversity (Slabbert et al., 2014). Native species diversity is lower in A. mearsnii invaded regions, possibly due to it allelopathic effects (Tassin et al., 2009). A. mearnsii invaded regions showed lower invertebrate species richness and diversity than uninvaded regions (Samways et al., 1996). A. mearnsii invaded soils generally had lower rhizobial diversity and was more homogenous compared to uninvaded soils (Le Roux et al., 2018). Native plant species richness decreased on all slopes invaded by A. mearnsii and soil became more acidic and nutrient rich (van der Waal, 2009). Soil moisture content was higher in invaded soils and diversity indices were higher in cleared and atural sites than in invaded sites (Ruwanza and Tshililo, 2019). A. mearnsii invaded sites had significantly lower species richness and taxonomic distinctiveness than cleared and uninvaded sites (Samways and Sharratt, 2010).