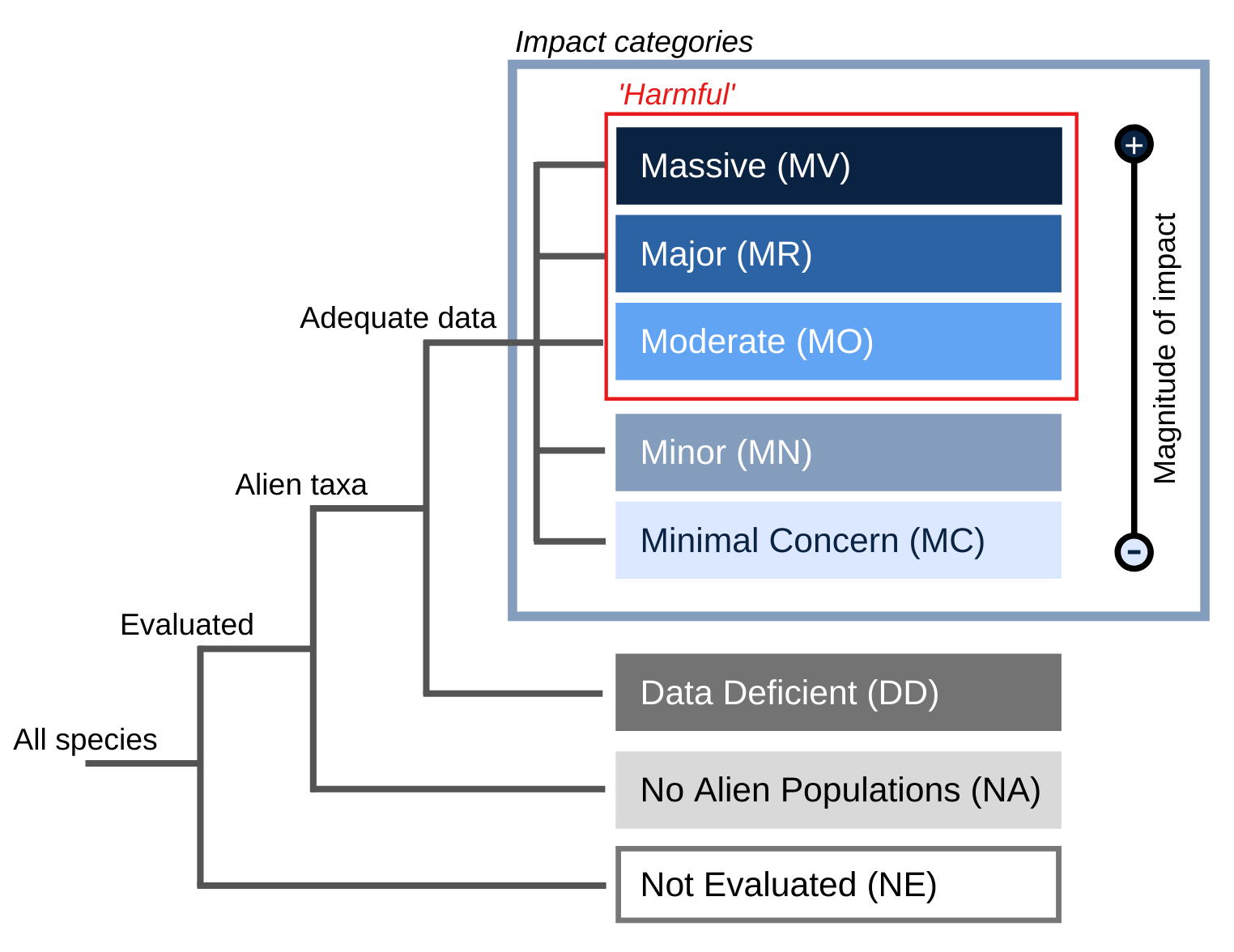
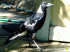- Not Evaluated
NE - No Alien Population
NA - Data Deficient
DD - Minimal Concern
MC - Minor
MN - Moderate
MO - Major
MR - Massive
MV
- General
- Distribution
- Impact
- Management
- Bibliography
- Contact
Principal source:
Compiler: IUCN/SSC Invasive Species Specialist Group (ISSG) with support from ASB Community Trust, New Zealand
Review:
Publication date: 2008-04-17
Recommended citation: Global Invasive Species Database (2026) Species profile: Gymnorhina tibicen. Downloaded from http://www.iucngisd.org/gisd/species.php?sc=1349 on 01-03-2026.
Physical: Physical removal of magpies can be achieved by shooting or trapping. Trapping often utilises mutton fat as a lure and a Larsen trap or a modified possum trap, which is essentially a spring loaded door that shuts as the bird enters the cage. Once inside, the trapped magpie can then be used as a lure for other birds which can then be put down by shooting (NRC, 1998).
Chemical: Poison is often used as a control, although it is not the most effective method. The poisonous bait consists of alphachloralose mixed with mutton fat, which renders the magpies unconscious and can then be easily killed (NRC, 1998).